Mobile data can add up, especially when you travel. Wi-Fi is hard to come by when you're on the go, and you usually rely more on mobile data to stay connected. But burning through data can get expensive, particularly if you're on a daily roaming plan.
But don't worry, we've got you! Here are ten tips to reduce data usage and stay connected when you travel.
1. Limit Background Data
One of the best ways to reduce data usage is to limit background data. Many apps continue to update and refresh in the background, even when you think you're offline. They sync emails, refresh social feeds, fetch photos and videos, and more. This keeps your apps up-to-date, but it also drains your data.
Here's how to turn off background data usage on your device.
For iOS devices:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap General.
- Tap Background App Refresh and turn it off.
For Android devices:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Connections > Data usage.
- From the Mobile section, tap Mobile data usage.
- Select an app from the usage graph.
- Turn off Allow background data usage.
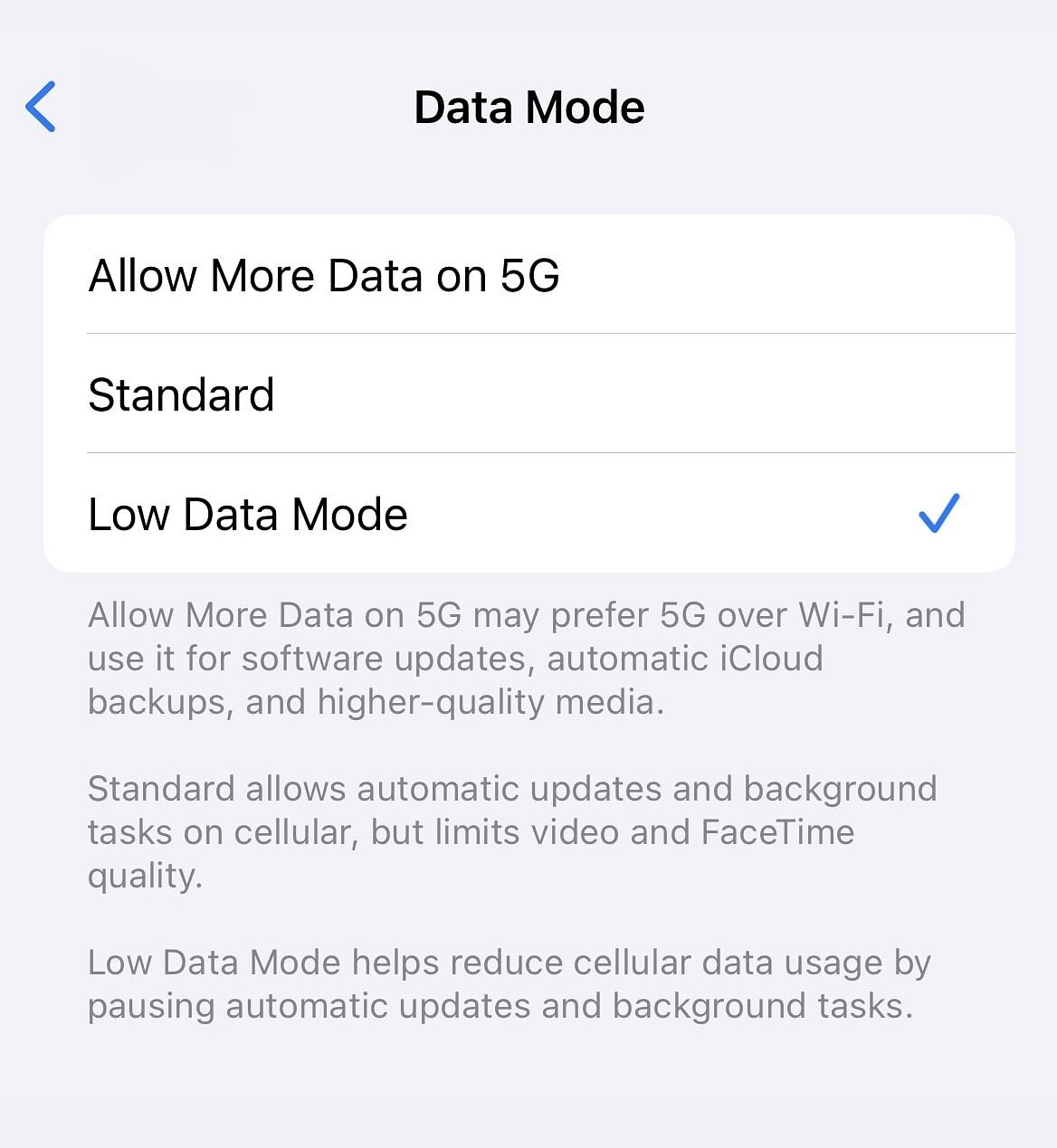
2. Use Low Data Mode on iPhone
If you have iOS 13 or later installed, you can turn on low data mode to reduce data usage. Apps will have different ways of restricting data, but in general, this is what you can expect:
- Apps will stop using data when you're not actively using them.
- Apps won't update or refresh in the background.
- Streaming quality will be reduced.
- Automatic downloads and backups will be turned off.
- Automatic updates will be paused (e.g., iCloud Photos).
Here's how to turn on low data mode for your iPhone:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Cellular > Mobile Data.
- Tap the phone line using data (if it's active, this will be your eSIM).
- Turn on Low Data Mode.
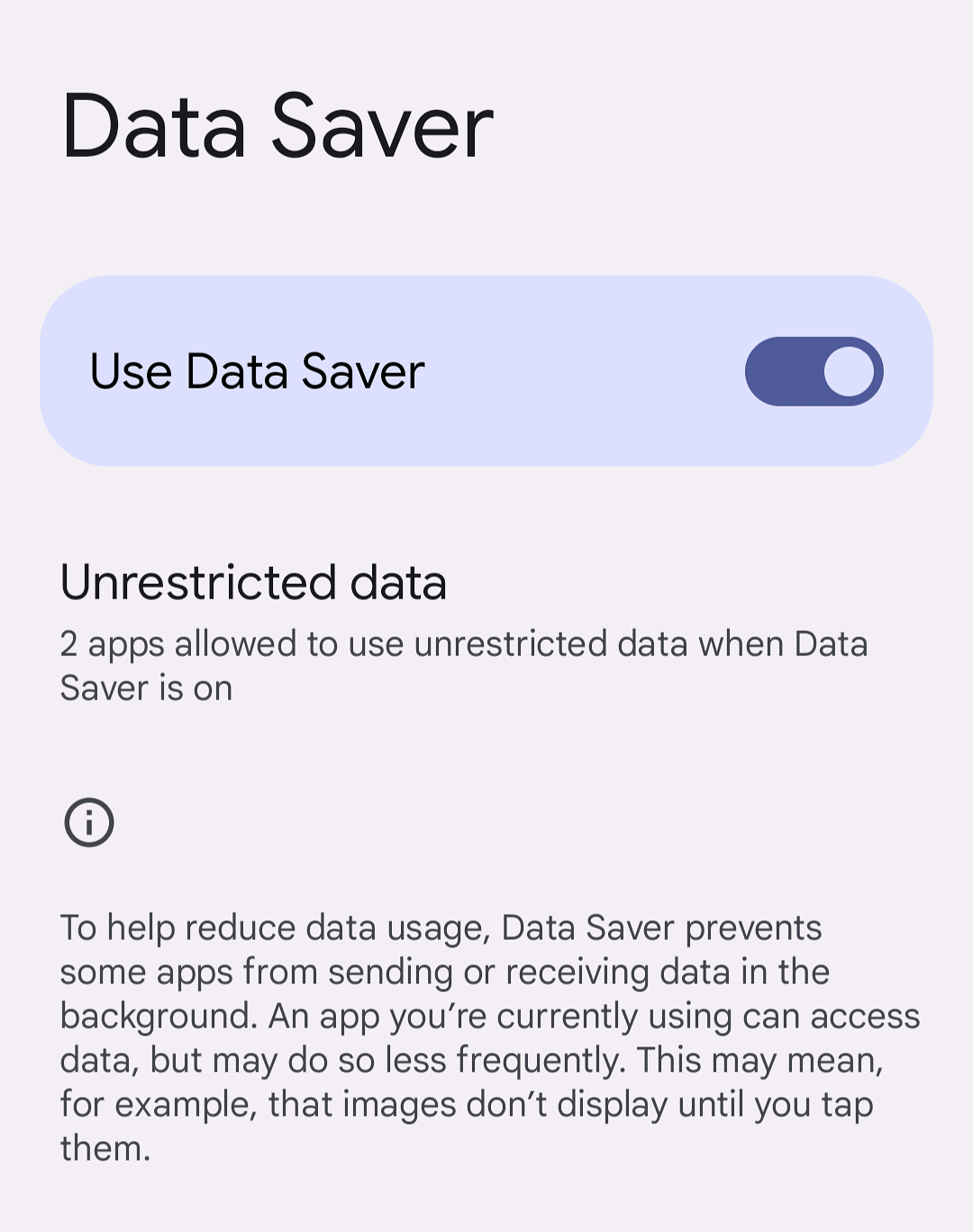
3. Use Data Saver Mode on Android
Android's data saver mode works the same way to reduce data usage. It limits what your apps can do in the background when you aren't connected to Wi-Fi. Switching on is easy and slightly different for Google and Samsung devices.
Here's how to turn on data saver mode for your Samsung smartphone:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Connections > Data Usage.
- Tap Data Saver.
- Turn on Data Saver.
And how to switch it on for your Google device:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Network & Internet.
- Tap Data Saver.
- Tap Use Data Saver.
4. Download, Don't Stream
Streaming services like Netflix, Spotify, and Apple Podcasts can quickly burn through data. For example, watching an episode of your favorite show in 4K can use up to 7GBs. Yikes.
However, most streaming apps have a download option. If you're heading abroad, you can download your favorite music, podcasts, and shows to your device before you leave. This will allow you to play them without needing an internet connection.
5. Take Maps Offline
Navigation apps like Google Maps are a must for any traveler. They make it super simple to orient yourself and get a lay of the land in a new location. The catch is they eat up data — especially when you're using them all the time.
If you're exploring a new city, consider taking Google Maps offline:
- Open Google Maps while you have a Wi-Fi connection.
- Search for your destination.
- At the bottom of the map, tap More > Download Offline Map > Download.
Once you've downloaded the map, you can continue using Google Maps like normal. You'll get turn-by-turn navigation to travel from point A to point B. And you'll use less data to get there.
6. Use Your Browser's Reading List
Another way to reduce data usage when you travel is to save web pages and articles to your browser's reading list. When you add a page to your reading list, your browser downloads it and makes it accessible for offline viewing. You can access it whenever and wherever — even if you don't have Wi-Fi or a mobile network signal.
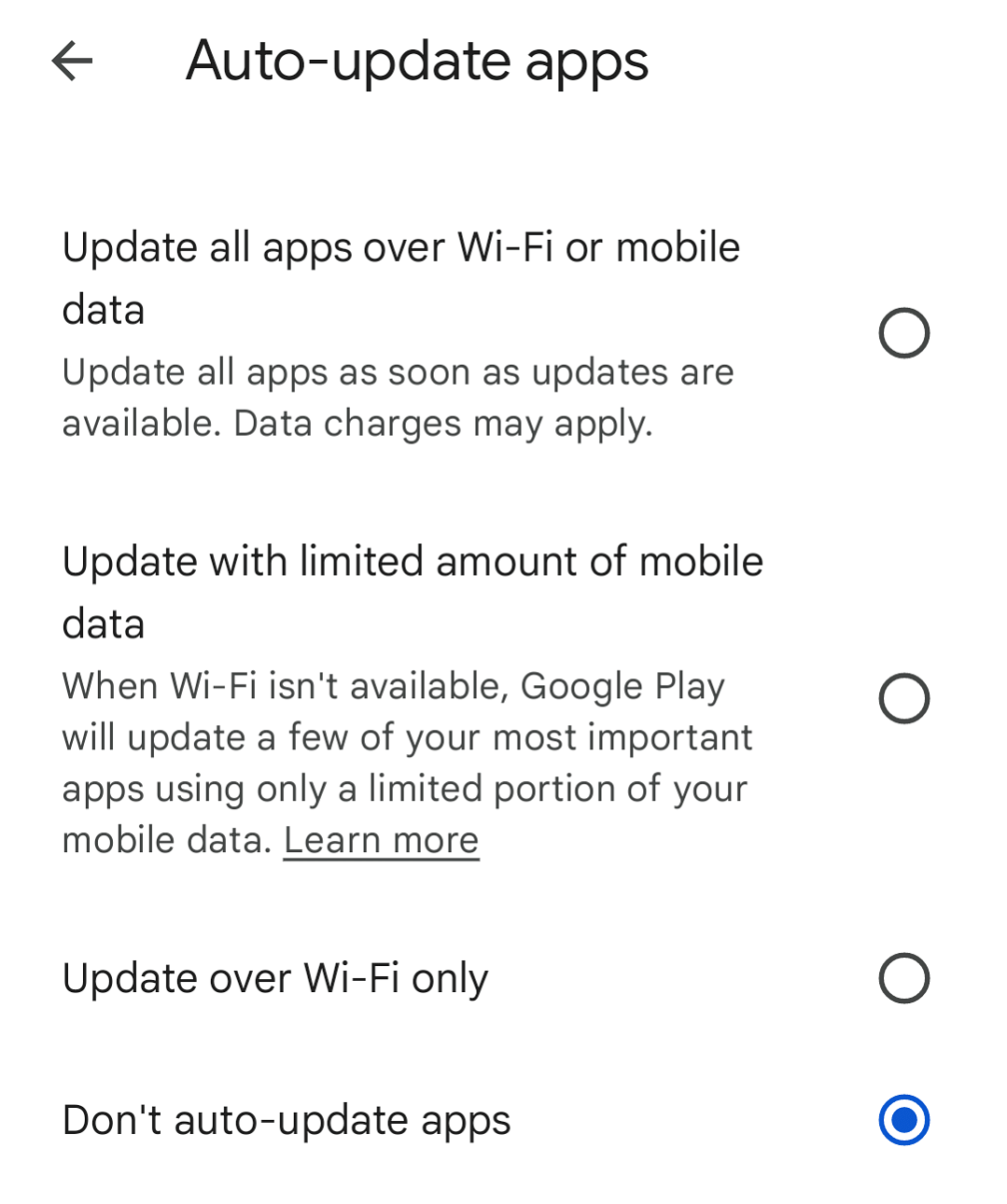
7. Disable Automatic Updates on Android
By default, auto-update is switched on for most Android smartphones. Whenever an app update is available, your Android device will automatically install it. Even if you're not connected to Wi-Fi.
Here's how to disable this feature in the Google Play Store:
- Open the Google Play Store app.
- Tap your profile icon to access the Menu.
- Select Settings > Network Preferences.
- Tap Auto-Update Apps.
- Tap Don't Auto-Update Apps or Over Wi-Fi Only.
- Tap Done to confirm.
8. Turn Off Wi-Fi Assist
You can also reduce data usage by turning off Wi-Fi Assist (or Network Switch on Android). Wi-Fi assist is enabled by default and ensures a stable network connection. When your Wi-Fi signal gets too weak or drops completely, it switches your connection to your cellular network. This is handy for your home network but can lead to unexpected roaming fees when you travel.
Here's how to turn off Wi-Fi Assist on your iPhone:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Mobile Data.
- Scroll to the bottom and turn off Wi-Fi Assist.
And how to turn off Network Switch on your Android:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Connections > Wi-Fi.
- Tap the three dots in the corner and select Advanced.
- Turn off Switch to mobile data.
9. Monitor Your Data Usage
Another tip to reduce data usage is monitoring what apps and activities use too much. In your device's settings, you can see a list of the apps you've installed and how much data they use. If an app is going overboard and you don't need it to travel, you might want to uninstall it or switch it off while you're away.
10. Travel Smart With an eSIM
Worried about roaming fees? You can use an Airalo eSIM to connect like a local in 200+ countries and regions worldwide. You'll get access to the best local networks at affordable rates and without hidden fees. And unlike your mobile provider, we won't let you exceed your data limit.
Airalo eSIM plans include a set amount of data (e.g., 1GB, 3GB, 5GB) for a set amount of time (e.g., 7 days, 15 days, 30 days). You can track your data usage in the Airalo app, and we'll send you notifications when you run low. Need to top up? No problem. You can buy a top-up or another eSIM right from your smartphone.
Where are you off to on your next adventure? Get an eSIM from Airalo to make the most of your mobile data and stay connected during your trip.
Editor's Note: This post was originally published in March 2023 and has been updated for accuracy.